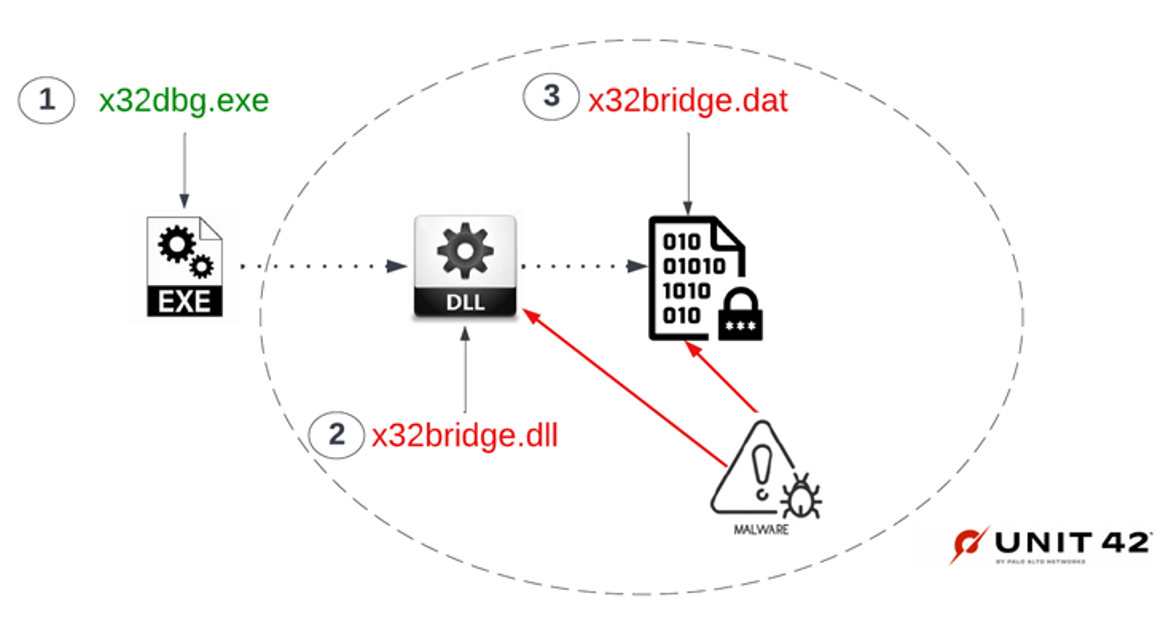
“This PlugX variant is wormable and infects USB devices in such a way that it conceals itself from the Windows operating file system,” Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 researchers Mike Harbison and Jen Miller-Osborn said. “A user would not know their USB device is infected or possibly used to exfiltrate data out of their networks.”
Tag: Malware
New attacks use Windows security bypass zero-day to drop Qbot malware
New phishing attacks use a Windows zero-day vulnerability to drop the Qbot malware without displaying Mark of the Web security warnings.
What is Triton malware and how it works
Introduction
Triton malware is a type of malicious software that is designed to target industrial control systems (ICS). It is a sophisticated piece of malware that is capable of disrupting the operations of industrial systems, such as those used in power plants, water treatment facilities, and other critical infrastructure. Triton malware is believed to have been developed by a nation-state actor and is capable of causing physical damage to industrial systems. In this article, we will discuss how Triton malware works and the potential risks it poses to industrial systems.
Exploring the Anatomy of Triton Malware: How It Works and What It Does
Triton malware is a sophisticated and dangerous form of malicious software that has been used in targeted attacks against industrial control systems (ICS). It is believed to have been developed by a nation-state actor and is capable of causing significant disruption to critical infrastructure. In this article, we will explore the anatomy of Triton malware and how it works to gain access to and manipulate ICS systems.
Triton malware is a type of malware known as a Remote Access Trojan (RAT). It is designed to gain access to a system by exploiting vulnerabilities in the system’s software or hardware. Once it has gained access, it can then be used to manipulate the system’s functions and data.
The first step in the process of Triton malware is to gain access to the system. This is done by exploiting vulnerabilities in the system’s software or hardware. Once access is gained, the malware can then be used to manipulate the system’s functions and data.
Once the malware has gained access to the system, it can then begin to manipulate the system’s functions and data. This is done by using a variety of techniques, such as modifying system settings, disabling security measures, and creating backdoors. The malware can also be used to collect data from the system, such as passwords and other sensitive information.
The final step in the process of Triton malware is to use the data it has collected to gain control of the system. This is done by using the data to create a backdoor into the system, allowing the attacker to gain access to the system without the user’s knowledge. Once the attacker has gained access, they can then manipulate the system’s functions and data to their own ends.
Triton malware is a dangerous form of malicious software that can cause significant disruption to critical infrastructure. It is capable of exploiting vulnerabilities in the system’s software or hardware to gain access and manipulate the system’s functions and data. By understanding how it works and what it does, organizations can take steps to protect their systems from this type of attack.
How Triton Malware is Used to Target Industrial Control Systems
Triton malware is a type of malicious software specifically designed to target industrial control systems (ICS). It is a sophisticated piece of malware that is capable of manipulating the operations of ICS, such as those used in power plants, water treatment facilities, and other critical infrastructure.
Triton malware is typically deployed through a phishing attack, in which an attacker sends a malicious email containing a malicious link or attachment. Once the user clicks on the link or opens the attachment, the malware is installed on the system. Once installed, the malware can gain access to the ICS and manipulate its operations.
Triton malware is designed to target the Triconex safety instrumented system (SIS), which is used in many industrial control systems. The malware is capable of manipulating the SIS in order to cause a disruption in the system’s operations. For example, it can be used to disable safety systems, which can lead to dangerous situations such as explosions or fires.
Triton malware is also capable of manipulating the ICS in order to gain access to sensitive data. This data can then be used to gain access to other systems or to launch further attacks.
Triton malware is a serious threat to industrial control systems and can have devastating consequences if not properly addressed. It is important for organizations to take steps to protect their systems from this type of attack, such as implementing strong security measures and regularly patching and updating their systems. Additionally, organizations should be aware of the signs of a potential attack and take steps to mitigate the risk.
Understanding the Impact of Triton Malware on Industrial Control Systems Security
Industrial Control Systems (ICS) are critical components of modern infrastructure, providing the necessary control and automation for a variety of industries, including energy, manufacturing, and transportation. Unfortunately, these systems are increasingly vulnerable to malicious attacks, as evidenced by the recent discovery of the Triton malware. This malicious software was designed to target ICS systems, and its impact on ICS security is significant.
Triton is a sophisticated piece of malware that was discovered in 2017. It is believed to have been developed by a nation-state actor, and its primary purpose is to target ICS systems. The malware is capable of manipulating the control systems of industrial facilities, allowing attackers to gain access to sensitive data and disrupt operations.
The most concerning aspect of Triton is its ability to manipulate ICS systems. By exploiting vulnerabilities in the system, the malware can gain access to the control systems and modify their settings. This could allow attackers to shut down critical systems, disrupt operations, or even cause physical damage to the facility.
The impact of Triton on ICS security is significant. The malware has demonstrated that ICS systems are vulnerable to attack, and that attackers can gain access to sensitive data and manipulate the control systems. This has raised concerns about the security of ICS systems, and has led to increased scrutiny of ICS security measures.
In response to the threat posed by Triton, organizations have implemented a variety of security measures. These include improved authentication and authorization protocols, increased monitoring of ICS systems, and improved patching and updating of ICS systems. Additionally, organizations have implemented security awareness training for personnel who work with ICS systems.
The impact of Triton on ICS security is clear. The malware has demonstrated that ICS systems are vulnerable to attack, and that attackers can gain access to sensitive data and manipulate the control systems. Organizations must take steps to ensure that their ICS systems are secure, and that personnel are aware of the risks posed by malicious actors. By taking these steps, organizations can protect their ICS systems from attack and ensure that their operations remain secure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Triton malware is a sophisticated and dangerous form of malware that is designed to target industrial control systems. It is capable of manipulating the system’s settings, allowing it to gain access to sensitive data and disrupt operations. It is important to be aware of the potential risks posed by Triton malware and to take steps to protect against it.