Small Error, Widespread Chaos: How CrowdStrike’s Update Shook the World
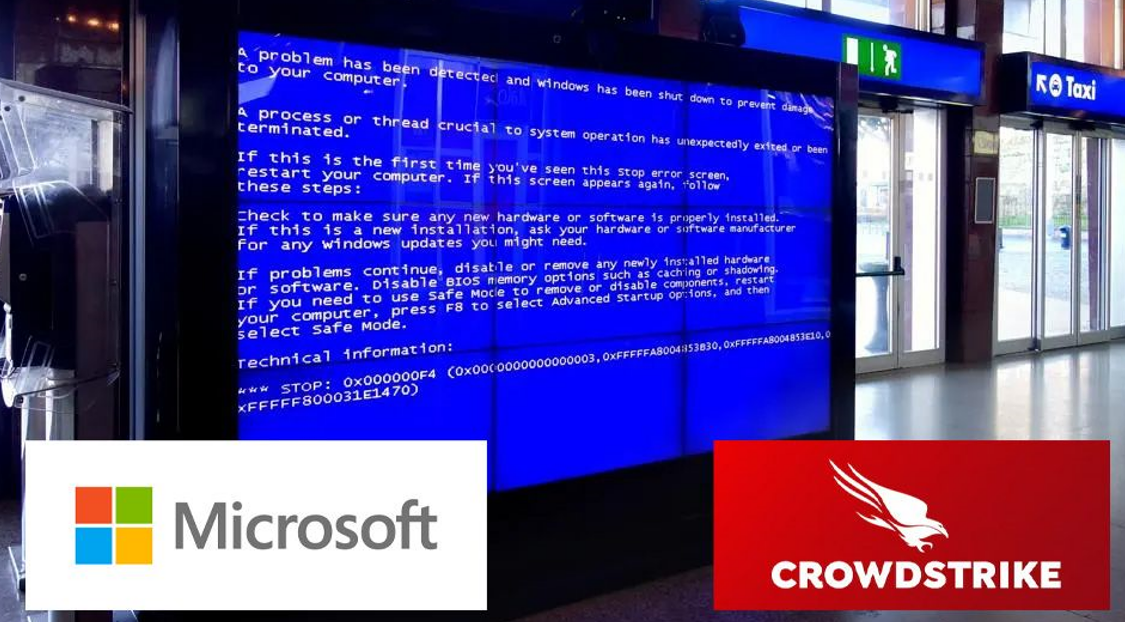
On Thursday, July 18, 2024, the world experienced one of the most extensive technological outages in recent history. American cybersecurity company CrowdStrike inadvertently distributed a faulty update to its security software, causing an estimated 8.5 million computers running Microsoft Windows to crash. These systems were left unable to properly restart, resulting in what has been called the largest outage in the history of information technology. The incident was caused by an external resource to the critical infrastructures.
CrowdStrike, an American cybersecurity firm, is known for its Falcon suite of security products designed to protect systems from cyber threats. On July 19, 2024, at 04:09 UTC, CrowdStrike released a configuration update for its Falcon sensor software that inadvertently triggered a catastrophic chain reaction.
What Happened?
Cause: The incident was triggered by a faulty configuration update for CrowdStrike’s Falcon driver software on Windows PCs and servers. The root cause of the incident was traced back to a logic error in the update. A logic error is a coding mistake that can cause a program to malfunction. In this case, the error triggered an operating system crash on Windows systems running the Falcon software.
The update contained a modification to a configuration file responsible for screening named pipes, specifically Channel File 291. This change led to an out-of-bounds memory read in the Windows sensor client, resulting in an invalid page fault, and causing systems to either enter a boot loop or boot into recovery mode.
The faulty update had a domino effect, with approximately 8.5 million Windows operating systems worldwide crashing, leading to a historic IT outage. The disruption affected a wide range of industries and services, including airlines, airports, banks, hospitals, and government agencies, with an estimated financial damage of at least $10 billion.
Fortunately, this event remained within IT environments and did not reach the OT infrastructure. Thanks God!
The root cause of the incident was traced back to a logic error in the update. A logic error is a coding mistake that can cause a program to malfunction. In this case, the error triggered an operating system crash on Windows systems running the Falcon software.
CrowdStrike did not test before deploying. Fatal combination of mistakes.
Impact: The outage disrupted critical services across various critical industries, including airlines, airports, banks, hotels, hospitals, manufacturing, stock markets, and broadcasting. Even governmental services and emergency websites were heavily affected.
Financial Damage: The worldwide financial damage has been estimated to range in the billions of dollars.
The flight systems were affected. Thousands of flights around the world were suspended. Collapse at airports. Millions of people were stranded, rescheduling of flights, delays in deliveries, logistics systems affected. The problem is not only that the planes could not take off, but that by that time there were thousands of planes in transit with the need to land. Critical flight timing was affected. Many companies still use outdated systems.
Banks were unable to transact business. The SWIFT System stopped working for three days. The billion-dollar bank transactions could not be carried out and by the end of the week they had to be rescheduled for the following week. In total there were three days for the non-working days of the weekend.
Approximately 8.5 million critical devices were affected. Less than 1% of all Microsoft devices in the world but managed by a single company. They all have a comon mode of failure. Lots of the most critical systems in the world were affected. Brazil was one of the most affected countries.
Then, who is accountable?
Microsoft did not take any responsibility. They attribute full responsibility to CrowdStrike for having been negligent in the application of the updates. Even though the patch released by Microsoft did not work properly. Where are all the controls mandated by government regulations? What are they for? Did they serve? Who is responsible and accountable? Microsoft, CrowdStrike, government regulations? All? And the end users? Aren’t they accountable?
These reminds me of the Ford-Bridgestone Explorer tire defect. Does someone remember what happened? Who was accountable? Ford, Bridgestone, or both?
And where is the forgotten Y2K campaign? Isn’t this single incident even worse than Y2K predictions?
Does someone know what was “The Eastland Disaster”. A wrongly implemented countermeasure, to prevent the Titanic tragic incident from repeating, which finally caused more death than the Titanic and the Lusitania together in only ten minutes. Do you find any similarity with the CorwdStrike incident?
The consequences for CrowdStrike following the 2024 incident were significant:
CrowdStrike has had a monetary impact on its shares due to the reliability of the market. Its shares lost 13% of their value. They finally delivered “candies” to the customers as compensation.
Verizon had serious difficulties keeping its communications services active. Thousands of users could not communicate. Some vehicles suddenly shut down. Thousands of global companies were affected that we don’t know yet about.
From a reputational point of view, this seriously affects diplomatic relations, trust in the systems that have generated a dependence on society, the economy and security. There has been a loss of confidence in institutions. The immediate damage and losses have been significant. However, I believe that this will have a much long-term impact.
Military application systems have also been affected. Defense systems may have been hit. Mac, Linux, or other operating systems were not affected. This does not mean that they cannot be affected in the future by similar situations.
Within hours, the error was discovered, and a fix was released. However, due to the need for manual fixes on each affected computer, outages persisted on many services. CrowdStrike produces security software products designed to protect computers from cyberattacks. The Falcon Sensor product, their vulnerability scanner, installs an endpoint sensor at the operating system kernel level to detect and prevent threats. Patches are routinely distributed to address new threats, but this update had unintended consequences.
In summary, the 2024 CrowdStrike incident serves as a stark reminder of how a small error can have far-reaching consequences in our interconnected digital world.
This is classified as a colossus critical infrastructure IT security incident and not as an OT incident. No direct physical impact has been reported yet, no impact over health, safety, environmental or industrial processes. May be there was but we still don’t know.
Reputation Damage: CrowdStrike’s reputation took a hit due to the widespread impact of the faulty update. Users and businesses questioned the reliability of their security solutions.
Financial Loss: The company faced substantial financial losses. Remediation efforts, customer compensation, and legal costs added up quickly. It has been estimated that the loss went over 10 billion dollars worldwide.
Legal Challenges: CrowdStrike faced potential lawsuits from affected organizations seeking compensation for damages incurred during the outage.
Operational Strain: The incident strained CrowdStrike’s operational resources as they worked to address the issue, communicate with clients, and provide fixes.
Despite these challenges, CrowdStrike took swift action to rectify the situation, improve their update processes, and regain trust. They remain a key player in the cybersecurity industry, but the incident serves as a cautionary tale for all end users, service providers and IACS vendors.
These incidents highlight the growing impact of cyber threats on organizations and underscore the need for resilient cybersecurity frameworks, such as ISA/IEC-62443 series of standards, developed by consensus of the global industry.
The Recommendations
What can be done to prevent these types of issues from happening into industrial OT environments?
The most important is that traditional cybersecurity and controls will always be insufficient and additional approaches such as consequence-based risk mitigation are needed. It does not matter how much money you can spend. It is about how much money you can save by investing in doing the right things right, instead of doing the wrong things perfectly well, repeatedly.
The primary solutions to prevent these types of incidents, are:
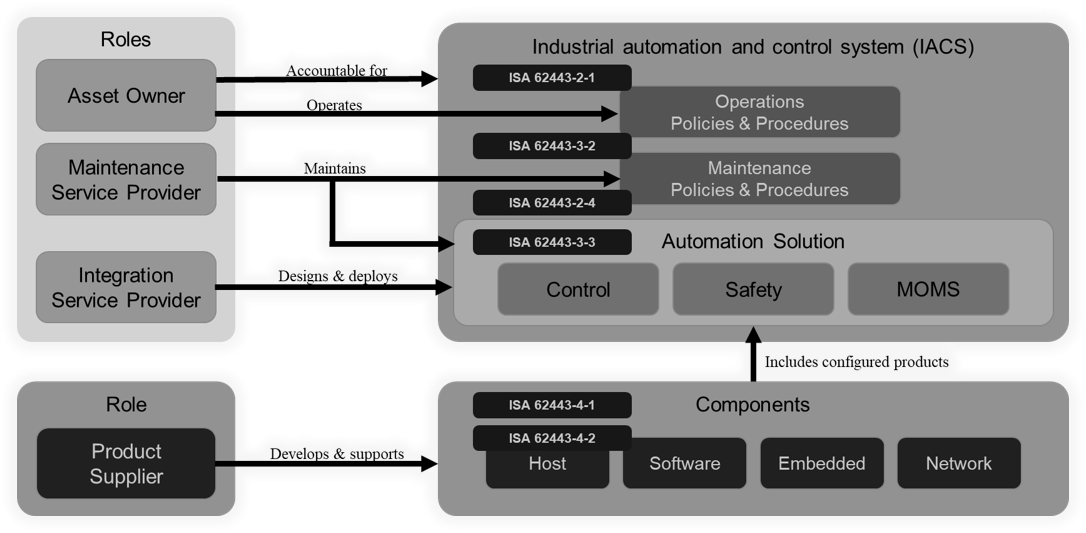
Assess the security practices of third-party vendors and partners. Ensure they meet the organization’s security policies and international standards. Service and solution providers should implement and comply with ISA/IEC-62443-2-4 set of requirements. Many vendors wrongly believe that having trained and certified professionals is enough, which is completely wrong.
The vendor must have Cybersecurity Managed Program in place in compliance with the ISA/IEC-62443-4-1. Their products should be certified in compliance with the ISA/IEC-62443-4-2. Proper testing needs to be executed before releasing an update to the market. Today’s vulnerability pressure and patch psychosis is forcing manufacturing companies to release patches quickly without testing them as they should be. Control systems require a lot more testing than traditional IT products.
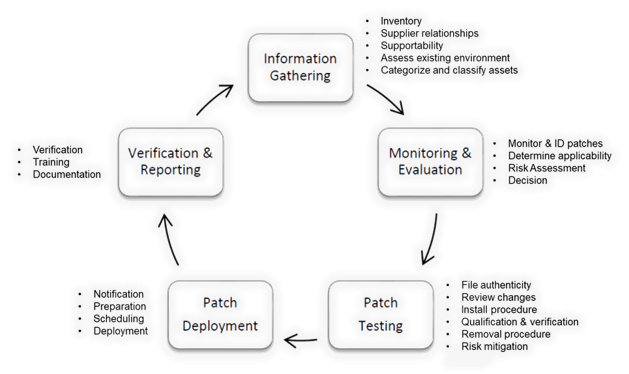
Implement a Patch Management Update procedure following the recommendations in compliance with the ISA/IEC-62443-2-3. Never apply a patch and especially “that wide deployment” on Fridays. That is a huge mistake. If something goes wrong, the resources to support and recovery will be extremely limited and a lot more complicated. Test the patches before deploying them into a running environment.
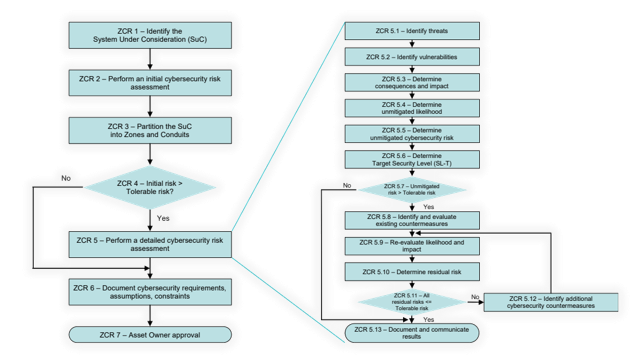
Segment zones and conduits in compliance with Foundational Requirements and Security Levels. Develop a modular Zones & Conduits risk management approach prioritizing correctly and rationally. The management of risk in industrial control systems is Bottom-Up in opposition to Top-Down as many IT security organizations and regulations are pushing it.
Regularly assess and prioritize risks related to cybersecurity by using a consequence-based approach such as ISA/IEC-62443-3-2. This security-by-design approach will allow production plants to prevent consequences from happening even if cyber incidents finally happen. Mitigate all intolerable risks as soon as possible. Avoid spending valuable resources on projects which do not mitigate the risk. Industrial control systems, their essential functions, and security should never depend or rely on external (cloud) solutions.
Independence of essential functions from cloud IIoT solutions. The report recently released by ISASecure is very insightfull. The more dependencies are created on external resources, the more vulnerable the plant will become this type of events. Read/Download here.
Secondarily, the following should be emphasized.
Take into consideration that the following recommendations do not prevent the incident from occurring, but they help reduce the impact of the consequences.
Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines steps to take during a security breach. Test the plan through simulated exercises to ensure effectiveness.
Regularly back up critical data and systems. Store backups securely and test restoration procedures. Consider offline or cloud-based backups to prevent ransomware attacks.
Remember that cybersecurity is an ongoing process, and staying vigilant is crucial.
Can we imagine or predict what could have happend if industrial controls systems were depending on CrowdStrike for the Updates?
Honestly, it is unthinkable. Surely, something like this affecting critical plants globally might have been created at least hunders of catastrophys, if not thousands. For now, it is only on the imagination. We are far from that scenario. Are we?
Why companies will continue to fail in mitigating the intollerable risks?
Basically because of two reasons.
(1) Companies fail to implement international standards. They know the standards but fail in the implementation.
(2) The upper management does not value international standards and insist in doing the wrong things or nothing.





Get Involved & Participate!
Comments